Table of Contents
ToggleISA 3.0 Project Report
Infrastructure Audit Report of A Bank Data Centre
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
A data center of the ABC Bank Ltd. centralizes and shares IT operations and equipment for the purposes of storing, processing, and disseminating data and applications. Data Center of the bank has the most critical and proprietary assets that are vital to the continuity of daily operations. This makes the security and reliability of data center and its information ABC Banks’ top priorities. The Infrastructure audit intends to determine whether ABC Bank Data Centre has identified:
1. Logical, physical and environmental threats.
2. Assessed the risk or impact presented by the threats.
3. Determined the feasibility of implementing controls to address the risks
4. Implemented appropriate controls, and re-assess risks periodically.
The Audit objective was to substantiate the internal controls of the data centre to mitigate risks. The audit objectives include assuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements as well as the confidentiality, integrity, reliability and availability of information and IT Resources. The purposes of Infrastructure IS audit was to identify control objectives and the related controls so as to express an opinion on whether the internal control system set up and operated by the data centre for the purpose of managing risks to the achievement of the objectives are suitably designed and operated effectively.
The Audit work includes interviews with data centre authorities & personnel, walkthroughs and inspections of the facilities, observations, and review of documentation and equipment configurations. We have reviewed safeguards to prevent unauthorized access to server operating systems and reviewed procedures to update and patch server operating systems. We reviewed physical controls, doorways, and access systems, monitoring functions, and the physical layout of the data centre. Our Audit work included reviewing controls over environmental threats and man-made threats.
Overall, there is not a process in place to ensure the continuity of data centre operations or for management to make an informed decision about the appropriateness, cost effectiveness, and necessity of implementing data centre controls. Data Centre has taken a minimal approach to securing the existing data centre. Data Centre performs damage control and remediation as problems arise, but does not eliminate or reduce all known threats proactively.
Our Audit report contains recommendations for the followings:
1. Implementing an overall process to ensure threats to the data centre are addressed.
2. Implementing safeguards over physical security to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Strengthening safeguards to mitigate threats.
4. Coordinating disaster recovery efforts and
5. Defining responsibilities for data centre security and coordination.
Our Audit report contains recommendations for the followings:
1. Implementing an overall process to ensure threats to the data centre are addressed.
2. Implementing safeguards over physical security to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Strengthening safeguards to mitigate threats.
4. Coordinating disaster recovery efforts and
5. Defining responsibilities for data centre security and coordination.
₹6,165.00
Limited Time Offer get 40% discount
Coupon “rajat40”
Courses Included




Information Systems Audit (ISA 3.0) – Video Lectures & Question Bank
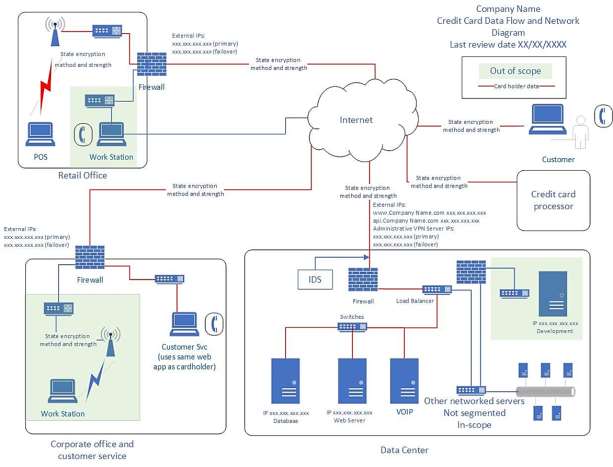
ABC BANK LTD.
The ABC Bank Ltd. Is regulated under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 and the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The main objectives of the Bank are:
1. To establish and carry on the business of a Banking Company
2. Lending/advancing money
3. Deal in securities both of its own and on behalf of the customers
4. Carry on and transact guarantee and indemnity business etc.
The data centre of the ABC Bank centralizes and shares IT operations and equipment for the purposes of storing, processing, and disseminating data and applications. Data Centre of the bank house most critical and proprietary assets that are vital to the continuity of daily operations. The security and reliability of data centres and their information are among Banks’ top priorities.
ABC Bank data centre is operated by 300 people out of whom 250 are from an outsourced company. There are 50 applications running including their core banking solution. Around 100 plus network devices like firewall, IDS, IPS, Router, Switches, Gateways etc. are there along with 500 plus high end servers. The asset register maintained by the bank is not updated and not reviewed for the last two years. It is difficult to get the idea of location and ownership of the asset. There is a Network operation centre (NOC), a building management system (BMS) and a security operation centre (SOC) separately placed along the data centre. All the infrastructures are managed by the outsourcing agency.
ABC Bank was having issues with access control mechanism. The menu access was not controlled by any authorization matrices. Anybody can access any menu in the core banking systems.
There were cases of violation of logical access control recorded in incident register but no follow-up action was made. In the data centre, the testing team and development team share the same server and at times with the permission of the system administrator they access the production system and implement the program. There is no librarian to maintain version control. Change management system is also not application driven and done manually. User access review being done once in a year. DBA team controls the patch management system and the network management team takes care of antimalware system. There are also issues with the management of backup tapes and blank tapes.
ABC Bank’s data centre needs a biometric access system, but the management feels that implementing biometric control to regulate entry of people in the data centre will be too costly and complex for them. They plan to appoint extra security guard as a compensatory control who is instructed to allow only those people into Data Centre who is having appropriate access card and also maintaining a register for entering access details which is supervised by the security officers.
THE ENVIRONMENT
A data center of ABC Bank centralizes shared IT operations and equipment for the purposes of storing, processing, and disseminating data and applications. Most critical and proprietary assets of the Bank are maintained at the data centers that are vital to the continuity of daily operations. The security and reliability of data centers and their information are among bank’s top priorities. The ABC Bank authorities want to assess the readiness of their operations for compliance with IT regulatory requirements for the efficacy of the bank’s Digital Assets, IT planning and implementation mainly for the following reasons
1. To check the Internal controls procedures of the information system in obtaining reliable and accurate information from the IT system for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity and continued availability of IT assets as the asset register is not maintained and updated by the bank regularly which makes difficult to get the idea of location and ownership of the asset.
2. The Network operation centre (NOC), a building management system (BMS) and a security operation centre (SOC) separately placed along the data centre. All the infrastructures are managed by the outsourcing agency.
BACKGROUND
The data center of the ABC Bank centralizes and shares IT operations and equipment for the purposes of storing, processing, and disseminating data and applications. Data Centre of the bank house most critical and proprietary assets that are vital to the continuity of daily operations. The security and reliability of data center and their information are among Banks’ top priorities.
The Bank authorities want to assess the readiness of their operations for compliance with IT regulatory requirements for the efficacy of the bank’s Digital Assets, IT planning and implementation. Bank wants to check the Internal controls procedures of the information system in obtaining reliable and accurate information from the IT system for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity and continued availability of IT assets.
CONTROL OBJECTIVES: (AREAS OF CONCERN)
INFORMATION SECURITY CONTROLS
Inadequate IS Security Policy implementation:
The Bank Security Policy appears to be a promotional document of Network Solutions restricted to System Administrators only and no other means of its dissemination to the operational staff.
Inadequate security at Data Centre:
There were no Physical Access Controls for safeguarding critical areas like Server room, Communication room, UPS room. The access control system installed was not functioning and no alternate arrangements had been made. Even though the Bank had a Security Policy, the doors did not have mechanical bolts/locks. Besides, access to a spare equipment room, which was also accessed by vendors, was through the Server room. Proper locking system at the main entry door (glass) was neither provided nor a Physical Security Officer appointed. The Head of Data Centre stated that the problems concerning improvement in infrastructure / security at Data Centre.
Inadequate Network Security:
Use of Internet in the Bank has exposed its Local Area Network (LAN) to outsiders, making it imperative to secure the network against unauthorized intrusion in order to protect information assets critical to the smooth operation and the competitive wellbeing of the Bank. The Bank had so far not put any Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) or Enterprise Security Solutions in place while opening up new services like e-Banking etc. to its customers.
Logical Access Controls:
The lack of security render the system vulnerable to unauthorized access. There are issues with access control mechanism. The menu access is not controlled by any authorization matrices. Anybody can access any menu in the core banking systems.
The violation of logical access control is inevitable. The testing team and development team share the same server and at times with the permission of the system administrator they access the production system and implement the program. In the Data Centre there is no librarian to maintain version control.
Inadequate Documentation and Change Management Control:
The bank is not maintaining proper documentation of activities such as backups, password changing (activation and deactivation), declaration from staff regarding maintaining secrecy of passwords, software problem register, AMC register, IT assets inventory register etc.
All system changes, whenever made, are not authorized at appropriate levels, documented, thoroughly tested and approved. No records were maintained for the changes made in the System or Application Software or the master data, from time to time especially the changes made in rate of interest on various schemes at the branch level.
The readability of the critical backup media is also not tested periodically for restorability. Lack of systematic procedure for regular backup and not regularly checking the usability of the backup has the risk of disruption in operations when the backup data are put to use.
Change management system is also not application driven and done manually. User access review being done once in a year. DBA team controls the patch management system and the network management team takes care of anti-malware system. There are also issues with the management of backup tapes and blank tapes
Inadequate IT Assets Inventory Management
The banks’ asset register is not maintained and updated by the bank regularly making it is difficult to get the idea of location and ownership of the asset.
TERMS AND SCOPE OF ASSIGNMENT:
Term of Assignment
The management of ABC Bank has approached us to perform an independent IS Infrastructure Audit of the bank’s data center for appraising the security and control practices so as to provide assurance to the management and regulators towards the readiness of the operations for compliance with IT regulatory requirements for the efficacy of the Bank’s Digital Assets, IT planning and implementation.
Scope of Assignment
The IS Audit assignment involves benchmarking of Data Centre operations with global best practices of security and controls, review compliance with banking rules as per regulations and review Process rules as applicable to Bank.
IS audit is expected to provide reasonable assurance to bank management by reviewing the availability, adequacy and appropriateness of controls so as to provide for a safe and secure computing environment for the bank and its customers.
The key objectives of IS Audit is to enhance the security of banking data center operations and provide assurance to management and regulators on availability of security and controls as per international best practices as applicable to banking.
The specific areas of audit includes the following:
1. Review of security and controls at each layer of system, network and database.
2. Review of all the key functionalities and related Security and Access Controls as designed at the parameter level.
3. Review how the banking process business rules and regulatory requirements have been designed and built in the package.
4. Review Applications covering functionalities and how these facilitate performance of process controls as per bank policy and regulations.
5. Mapping of best practices of security and controls to evaluate the design of security and control.
The overall objective of the IS audit of bank data center is to ensure that the following seven attributes of data or information are maintained:
1. Effectiveness in dealing with information being relevant and pertinent to the business processes as well as being delivered in a timely, correct, consistent and usable manner.
2. Efficiency concerning the provision of information through the optimal (most productive and economical) usage of resources.
3. Confidentiality concerning the protection of sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure.
4. Integrity related to the accuracy and completeness of information and its validity in accordance with the business’ set of values and expectations.
5. Availability related to information being available when required by the business process, and also concerned with the safeguarding of resources.
6. Compliance with laws, regulations and arrangements essentially meaning that systems need to operate within the ambit of rules, regulations and/or conditions of the organization.
7. Reliability of information.
LOGISTIC ARRANGEMENTS REQUIRED
The logistics required for performance and discharge of our audit obligations are as follows:
1. Standard Operating Manual in use, Procedure, Duty Delegation and Organization Chart as well as the reporting mechanism.
2. Operating documentation and records such as prior audit reports and corrective action taken report.
3. Security Policy
4. Vulnerability assessment of Infrastructure relating to CBS Network, Data Centre
5. Assets Register – Scrutiny of documents relating to development, implementation, procurement of hardware and software.
7. Minutes of the Steering Committee.
8. Various Frameworks, Laws, Regulations as implanted at the bank and the data center
9. Service Level agreements with the outsourcing agencies/service providers etc.
10. Risk Register.
11. Interaction and interview of Human resources at key position at the data center.
12. Physical Infra Structure of the Data Center.
13. Travel & living arrangements (Audit team members).
14. Audit plan pre-approval.
15. Audit authorization: memo, letter, schedule.
AUDIT DETAILS (TIME LINE)
We have been provided list of key security and control practices and are required to review the
adequacy of these control practices and also provide additional detailed procedures as relevant to
Indian regulations considering Information Technology Act and other compliances applicable for Indian
banking companies. We have conducted and reviewed the following documents and procedures for
the purpose of our audit and framing our report.
- Vulnerability assessment of Infrastructure relating to CBS Network, Data Centre.
- Functional audit for reviewing the maintenance of a well-controlled (Physical & Logical) environment, and Data Centre covering Parameter / Access / Back end corrections /Change Management.
- Testing of the general IT controls.
- Testing of application controls in IT applications running in the Bank’s Data Centre
- Risk Identification and Management(Threats & Vulnerabilities)
- IT Governance (Management participation)
- Scrutiny of documents relating to development, implementation, procurement of hardware and software.
- Disaster Recovery Plan and Procedure
- Backup Policy
- Compliance Testing: Scrutiny of IT security policy adopted and implemented by the Bank.
- Substantive Testing: Analysing and checking the bank database for assessing completeness, correctness and reliability of data.
- Testing of application controls in IT security system.
- Interaction with the Management.
- IT Control Audit: General and Application Controls
- Understanding of IT Resources deployment
- Understanding of the IT Strategy and internal control system
- Review of IT Outsourcing Policy
- Identification and documentation of IT related Circulars
- Identification and documentation of Organisation Structure and Information Architecture
- Assessing the performance of the bank data centre against:
-
- a. COBIT-19 Framework with regard to acquisition and maintenance of Assets and implementation of IT.
- b. Circulars/Instructions /Policy regarding Banking Operations and IT policy
- c. Security policy of the Bank and
- d. RBI guidelines on various issues like in-operative accounts, Anti money laundering policy etc.
AUDIT PROCEDURE:
Audit of IT Controls at the Data Centre:
IT controls can be classified as:
1. General Controls
2. Application Controls.
General IT controls are concerned with the organization’s IT infrastructure, including any IT related policies, procedures and working practices.
General controls include controls related to:
1. Data centre operations,
2. System software acquisition and maintenance,
3. Access security, and
4. Application system development and maintenance.
5. Organization and management controls (IT policies and standards).
6. IT operational controls.
7. Physical controls (access and environment).
8. Logical access controls.
9. Acquisition and program change controls.
10. Business continuity and disaster recovery controls.
For accessing the General Controls we have reviewed the followings:
1. IT policies, standards, and guidelines pertaining to IT security and information protection.
2. Application software development and change controls,
3. Segregation of duties,
4. Business continuity planning policy,
5. IT project management
Application IT controls are specific computer application controls. They include controls that help to ensure the proper authorisation, completeness, accuracy, and validity of transactions, maintenance, and other types of data input.
Application controls include controls related to:
1. Controls over the input of transactions.
System edit checks of the format of entered data to help prevent possible invalid inputs.
2. Controls over processing.
System enforced transaction controls preventing users from performing transactions that are not part of their normal duties.
3. Controls over output.
Creation of detailed reports to ensure all transactions have been posted completely and accurate. Controls over standing data and master files.
Procedure adopted for Auditing of General and Application IT Controls at the Data Centre
1. Our audit team have personally monitored the day to day performance of the system at the data centre in terms of measuring the
1. Response time.
2. Initial Program loading for booting up the systems.
3. Media Management for control of devices
4. Job Scheduling and processing
5. Back-ups of data and software.
6. Maintenance of both hardware and software.
7. Network Monitoring and Administration.
Our audit team has reviewed and discussed Service Level Agreement with the other departments of the bank and the data centre operations for specifically understanding and agreement of levels of service, in terms of quantity and quality.
We have given consideration to following point while reviewing the SLA.
1. General provisions including the scope of the agreement, its signatories, date of next review.
2. Brief description of services.
3. Service hours.
4. Service availability (percentage availability, maximum number of service failures and the maximum downtime per failure);
5. Performance (response times, turnaround times);
6. Security and Restrictions
Audit of Physical Control (Access and Environment) of the Data Centre:
The objective of physical and environmental controls is to prevent unauthorised access and interference to IT services. In meeting the objective computer equipment and the information they contain and control should be protected from unauthorised users. They should also be protected from environmental damage.
Control Objectives & Procedure adopted for Auditing of Physical Access Controls at the Data Centre:
Checklist for verifying the Physical Access Controls
The Logical access controls are for protecting the applications and underlying data files from unauthorised access, amendment or deletion by limiting access and ensuring:
1. Users have only the access needed to perform their duties.
2. Limited access to sensitive resources such as security software program.
Logical access controls depend on the in-built security facilities available under the operating system or hardware in use.
Our audit Team has reviewed the most common form of logical access control that is the login
identifiers (ids) followed by password authentication. For passwords to be effective there must be
appropriate password policies and procedures, which are known to all staff and adhered to.
Control Objectives & Procedure adopted for Auditing of Logical Access Controls at the Data Centre
Checklist for verifying the Logical Access Controls
Audit of Network Control of the Data Centre
The Network Controls are for controlling the access the network resources only to authorised users. Control of networks is not just about logical access security.
Networks are primarily used to transmit data. When data is transmitted, it may be lost, corrupted or intercepted. Our audit Team has reviewed the Network access controls to reduce all these risks. We have reviewed the followings for the above purpose:
1. Network security policy. It was part of the overall IT security policy
2. Network documentation describing the logical and physical layout of the network
3. Logical access controls.
Control Objectives & Procedure adopted for Auditing of Network Controls at the Data Centre
Checklist for verifying the Network Controls
Audit of Firewall Control of the Data Centre
The Firewall Controls are for controlling traffic between the corporate network and the Internet and
also the access to the network resources. Firewalls are set up to allow only specific Internet services
and may provide additional services such as logging, authentication, encryption and packet filtering.
Control Objectives & Procedure adopted for Auditing of Firewall Controls at the Data Centre
Checklist for verifying the Firewall Controls
DOCUMENTS REVIEWED
No. List of documents
1 Background of the ABC Bank and the Data Centre
2 ABC Bank’s Organizational chart
3 HR Personnel policy
4 Regulations and laws that affect the organization (for example – COBIT-19)
5 Security Policy
6 Networking Policy
7 Systems manual, User manual and Operations manual
8 List of applications and their details
9 Network and application architecture, including client- server architecture
10 Organizational structure of the IT department with job descriptions
11 IT department’s responsibilities with reference to the specific application
12 Project management reports
13 Different Service Level Agreements – SLAs
14 Asset register for details of hardware
15 Details of software
16 Database details – Schema, Data Flow Diagram, Data Dictionary, Table listings
17 Details of interfaces with other systems
18 Performance analysis reports
19 List of users with permissions
20 Test data and test results
21 Security set up for the system
22 Internal audit reports
23 Previous audit reports
24 User feedback about the system
25 Peer review report
PROCESSES REVIEWED
Processes describe organized set of practices and activities to achieve certain objectives and produce a set of outputs in support of achieving overall IT-related goals.
During the course of our audit for better understanding our team has reviewed and done walkthrough the data center process model for the following components:
1. Application security
2. Cryptography
3. Monitoring
4. Incident management
5. Online banking security
6. Malware management
7. Data protection
8. Vendor (third-party) management
9. Business continuity planning
10. Privacy
11. Identity and access management
12. Risk management
13. Physical security
14. Awareness
15. Governance
16. Policy and Procedures
17. Asset life cycle management
18. Accountability and ownership
19. System configuration
20. Network security
We found that each of the components contributes to building the control standards and control procedures that satisfy high-level policy requirements.
We have followed bottom-up approach that serves to mitigate the top-level security concerns for bank’s data center processes by providing adequate security for the assets used by these processes.
REFERENCES
COBIT – 19
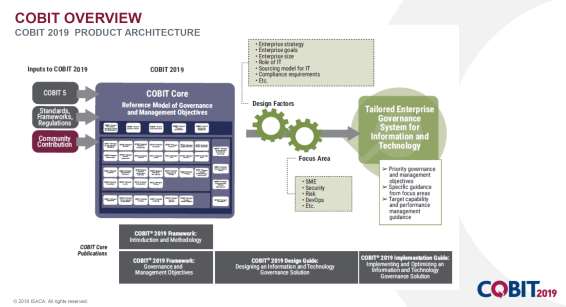
COBIT is a framework for the governance and management of enterprise information and technology, aimed at the whole enterprise. COBIT describes enablers, which are factors that, individually and collectively, influence governance and management of organization:
1. Principles, policies and frameworks are the vehicles to translate a desired behavior into practical guidance for day-to-day management.
2. Processes describe an organized set of practices and activities to achieve certain objectives and produce a set of outputs in support of achieving overall IT-related goals.
3. Organizational structures are the key decision-making entities in an enterprise.
4. Culture, ethics and behavior of individuals and the enterprise are often underestimated as a success factor in governance and management activities.
5. Information is pervasive throughout any organization and includes all information produced and used by the enterprise. Information is required for keeping the organization running and well governed, but at the operational level, information is often the key product of the enterprise.
6. Services, infrastructure and applications include the infrastructure, technology and applications that provide the enterprise with IT processing and services.
7. People, skills and competencies are linked to people and are required for successful completion of all activities and for making correct decisions and taking corrective actions.
ABC bank was in the process of implementing a model in which COBIT can be used to meet the followings:
1. IT performance,
2. Audit and compliance requirements within the bank.
3. Creating a Risk Management Model
We were explained by the Bank the importance of a holistic approach, using COBIT enablers toward building a sustainable IT governance and risk management model for the bank.
The implementation was not complete.
ONLINE RESOURCES & REFERENCES:
1. COBIT – 19 Toolkit
https://www.isaca.org/resources/cobit
2. COBIT® 2019 Framework: Introduction and Methodology
COBIT® 2019 Framework: Governance and Management Objectives
https://www.isaca.org/bookstore/bookstore-cobit_19-digital/wcb19fim
3. COBIT® 2019 Design Guide: Designing an Information and Technology
https://www.isaca.org/bookstore/bookstore-cobit_19-digital/wcb19dgd
4. COBIT® 2019 Implementation Guide: Implementing and Optimizing an Information and Technology Governance Solution
https://www.isaca.org/bookstore/bookstore-cobit_19-digital/wcb19igio
DELIVERABLES
We have conducted an information systems audit of Data Center operations. Our audit focused on the management and protection of the central data center against physical, logical threats.
Our Audit Report contains five categories of recommendations addressing:
1. Implementing an overall process to ensure threats to the data center are addressed.
2. Implementing safeguards over physical security to deter unauthorized access.
3. Strengthening safeguards to mitigate threats.
4. Coordinating disaster recovery efforts.
5. Defining responsibilities for data center security and coordination.
We wish to express our appreciation to the department for their cooperation and assistance.
AUDIT FINDINGS
Audit Opening Remarks:
We have conducted the audit for determining whether the Bank has identified logical, physical threats to the data center, assessed the risk or impact presented by the threats, determined the feasibility of implementing controls to address the risks, implemented appropriate controls, and re-assess risks periodically.
Our Audit work included interviews with bank personnel, walkthroughs and inspections of the facilities, observations, and review of documentation and equipment configurations. We reviewed safeguards used to prevent unauthorized access to server operating systems and reviewed procedures to update and patch server operating systems. We reviewed physical controls, doorways and access systems, monitoring functions, and the physical layout of the data center.
FINDINGS – HIGHLIGHTS:
Data Center has controls in place for fire and heat, power surges and outages, and operating systems access and updates. In the areas of physical security controls are fragmented or nonexistent and can be improved.
Overall, there is not a process in place to ensure the continuity of data center operations or for management to make an informed decision about the appropriateness, cost effectiveness, and necessity of implementing data center controls. Data Center Infrastructure Cannot Easily Adapt to Changes in Operations.
Our audit reviewed the areas of:
1. Planning and Management,
2. Physical Security,
3. Environmental Security, and Recovery and Incident Response.
4. Details regarding controls in these areas.
The details regarding controls in these areas and conclusions are as follows:
1. Inadequate Physical Facilities
Physical and Network security was inadequate at the Bank’s critical Data Centre.
2. Inadequate/lack of Disaster recovery Plan
The 20 Core Banking Solution branches are being run without any Disaster Recovery Plan thereby exposing the system to the risk of disruption of its operations in the event of any disaster. Bank has controls in place for fire and heat, power surges and outages, and operating systems access and updates. In the areas of physical security, the controls are fragmented or nonexistent and can be improved.
Bank performs damage control and remediation as problems arise, but does not eliminate or reduce all known threats proactively.
3. Improper maintenance of Assets Register
The Asset Register is not maintained by the Bank and Data Center makes it difficult to ascertain the location of the assets.
4. Inadequate IS Security Policy implementation.
We have observed during audit that Bank had not formulated any Security Policy until 2015. In February 2015, an Information System Security Policy was formulated which appeared to us to be a promotional document of Network Solutions rather than an internal document of the Bank.
The policy documents was kept on Bank’s intranet site which is restricted to System Administrators only and no other means of its dissemination to the operational level were adopted. This inadequate dissemination of the policy at branch level resulted in most of the staff being ignorant of this policy.
5. Inadequate security at Data Centre
There were no Physical Access Controls for safeguarding critical areas like Server room, Communication room, UPS room. The access control system installed was not functioning and no alternate arrangements had been made. Even the doors did not have mechanical bolts/locks. Besides, access to a spare equipment room, which was also accessed by vendors, was through the Server room. Proper locking system at the main entry door (glass) was neither provided nor a Physical Security Officer appointed. Security Cameras were also inadequate.
There was no Annual Maintenance contract for critical systems like access lock system, CCTV, fire alarm, firefighting system. The UPS installed at Data Centre had never been tested for fault tolerance.
6. Inadequate Logical Access Controls
During the course of our audit we found that default passwords were running and had not been changed by System Administrator. No undertaking from users for maintaining the confidentiality of password was not obtained.
7. Inadequate Network Security Controls
During the Audit, we observed the following security deficiencies in the network:
a. There wasn’t any Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) or Enterprise Security Solutions in place for services like e-Banking etc. to its customers.
b. Network penetration testing was not conducted by an independent agency. Instead the Bank had got “Internet Banking Security Assessment” done from the vendor for all their networking projects.
c. Data Center had not adopted Network Time Protocol (NTP) for synchronization of all routers in case of power disruption.
8. Inadequate Documentation and Change Management Control.
Effective preparation, distribution, control and maintenance of documentation is helpful in reuse, conversion, correction and enhancement of the IT system.
During the course of Audit we found slackness in maintaining the proper documentation of various activities such as backups, password changing (activation and deactivation), declaration from staff regarding maintaining secrecy of passwords, software problem register, AMC register, IT assets inventory register etc.
9. Poor implementation of Backup Controls
We observed that, a back-up policy had been adopted by the Bank and the backups were being taken at regular intervals (daily, weekly, fortnightly), but the procedures associated with documentation, safe custody and testing were not being uniformly implemented as proper backup registers depicting the daily backup processes and storage and testing details had not been maintained.
10. Inadequate Application specific Controls:
a. Inadequate control over inoperative Accounts
b. Incomplete/incorrect data migration
11. Inadequate robust and transparent acquisition policy resulting in non-competitive purchases and ad hoc procurements
RISK ASSESSMENT / RECOMMENDATIONS
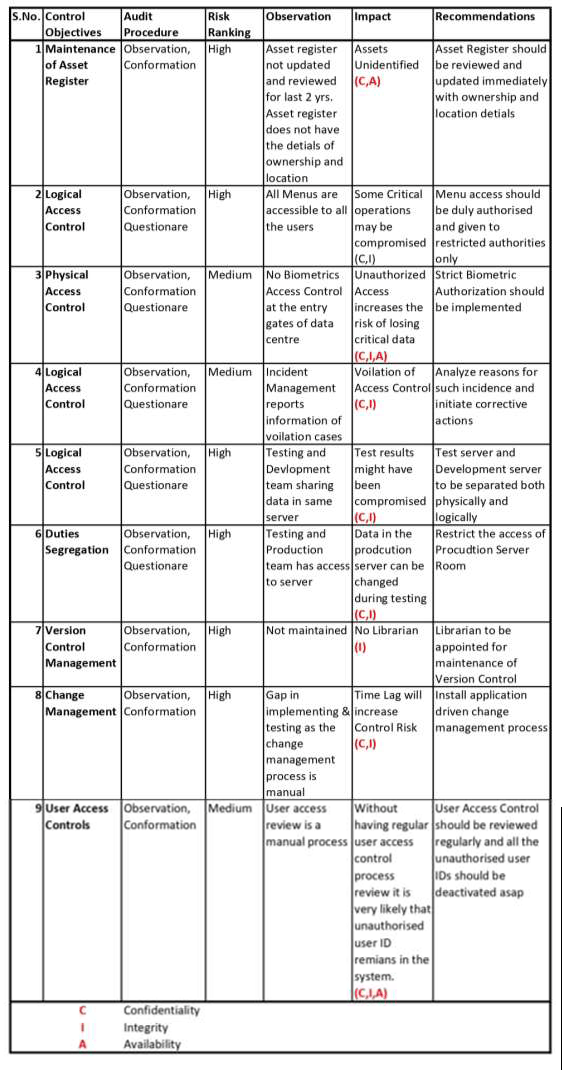
RISK RANKING
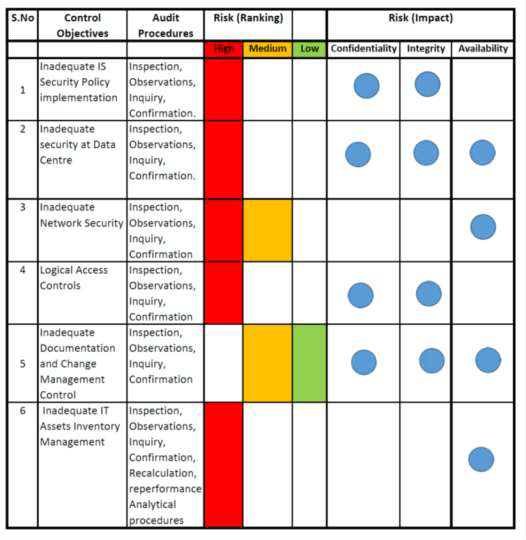
SUMMARY/CONCLUSION
The objective of our audit of data center was to evaluate against applicable standards to ensure the security and availability of technology assets and to provide information technology services. We are pleased to conclude the results of our audit.
The audit revealed that ABC Bank need to address several issues and improve their data center operations. The Data Center needs to implement new controls over the management of critical data center facilities.
The operations of Data Center can be improved by addressing weak environmental controls, by improving ongoing software application reviews, and by implementing cost accounting practices. In addition, developing and implementing policies and procedures for technology infrastructure will help Data Center prevent system failures that could cause a loss of data? Our report lists several related recommendations to address these concerns. In addition, we identified security-related findings, which have been communicated separately to management of Bank and the Data Center.
Our Audit Report contains five categories of recommendations addressing:
1. Implementing an overall process to ensure threats to the data center are addressed.
2. Implementing safeguards over physical security to deter unauthorized access.
3. Strengthening safeguards to mitigate threats.
4. Coordinating disaster recovery efforts.
5. Defining responsibilities for data center security and coordination.
RECOMMENDATIONS:
1. Data Center must “implement appropriate cost-effective safeguards to reduce, eliminate, or recover from identified threats to data.” Data Center has the custodial responsibility to protect the data center with safeguards proportional to the importance of the equipment residing in the data center and the extent of potential loss. Data Center must identify what equipment it is protecting, threats to the equipment, potential safeguards, and associated costs to implement the safeguards.
2. Data Center must plan for their assets and operations and sets the tone for the level of protection by understanding what equipment and systems reside in the data center, knowing where the responsibility for protection lies, knowing what controls are in place and what are lacking, and mitigating the identified threats to the extent possible.
3. Access policy should be periodically reviewed to ensure the approved security level is maintained
4. Maintain and update the inventory of equipment, systems, and data residing in the data center.
5. Coordinate with all agencies that have hosted systems in the data center to rank the systems’ criticality and establish a priority.
6. Evaluate existing threats to the data center including the potential impact or harm.
7. Conduct a cost analysis associated with implementing or improving controls.
8. Define the responsibility for, and coordinate with agencies to utilize the existing software package to develop disaster recovery plans.
9. Implement safeguards such as locked doors in the Data Center building.
10. Implement procedures and assign responsibilities for ensuring background checks are complete.
11. Follow Security policy and maintain required authorization documentation on file for each individual who has access to the data center.
12. Conduct a periodic review of all key card access to the data center to confirm appropriateness.
13. Monitor and review card activity logs and data center visitor logs for inappropriate or unauthorized access.
14. Develop a system to ensure operator awareness of physical security breaches.
15. We recommend the Data Center to strengthen safeguards to mitigate the environmental risks.
16. We recommend the Data Center to clearly define and designate responsibility for coordination of all aspects of data center security.
17. We recommend the Data Center to maintain an updated disaster recovery plan.
We wish to express our appreciation to the various bank department for their cooperation and assistance.
DISA 3.0 Project Report on:
1. IS Audit of Banking Application
2. Migrating to cloud based ERP solution
3. Security control review of railway reservation system
4. Review of Cyber Security Policies and Procedures Disa ICAI Project Report ISA 3.0
5. Disa Project Report on Security and Control Risk assessment of Toll Bridge operations
6. System audit of a hospital automation system
7. Review of vendor proposal for SaaS services
8. Information Systems audit of a mutual fund systems
9. Audit of outsourced software development
10. Network security audit of remote operations including WFH
11. Conducting vulnerability assessment and penetration testing
12. Auditing Business continuity plan for Manufacturing system
13. Assessing risk and formulating policy for mobile computing
14. Auditing robotic process automation system
15. Implementation of adequate governance in hotel management system
16. Outsourced migration audit of merger of Banks
17. Audit of an E-Commerce web site
18. Audit of Online booking system for a hotel chain
19. Audit of Business Continuity Planning of a financial institution
20. Audit of online brokerage firm
21. Audit of Security Operation Centre of a Bank
22. Audit of Cyber Security Framework of a PSB
23. EVALUATION OF OUTSOURCING IT OPERATIONS
24. Auditing SWIFT operations in a Bank
25. Project Report Template and Guidelines on Project Report Submission
26. Information Systems Audit of ERP Software
27 .Implementing Grc As Per Clause 49 Listing Requirements
28. Review of IT Security Policies and Procedures in audit
₹6,165.00
Limited Time Offer get 40% discount
Coupon “rajat40”
Courses Included




Information Systems Audit (ISA 3.0) – Video Lectures & Question Bank
