Table of Contents
ToggleDetails of Case Study/Project (Problem)
Indian railway online ticketing Scam
“On Track Limited” has identified the major problem regarding illegal operations to book tatkal tickets of Indian Railways in illegal manner. Railway has then ongoing drive against ticket less travelers and such illegal ticket booking, which creates artificial shortages of tickets. There are so many instances found for fraud booking in name of IRCTC.
Also, the bug detected that attackers have access to passenger details such as name, age, gender and insurance nominees without their knowledge and consent implying threat for loss of confidential data.
Introduction
“On Track Limited” is governmental entity under the Ministry of Railways which operates India’s national railway system. It facilitates user registration/login for booking online railway tickets, checking availability of trains and seats, provisions for Tatkal Tickets booking, general booking system and thus manages users and maintaining the database for users and transactions. It also provides platform for passenger to enquire about their ticket confirmation or cancellation, refund status and train enquiry facility.
Structure
Indian Railways is headed by a seven-member Railway Board whose chairman reports to the Ministry of Railways. Railway Board also acts as the Ministry of Railways. The officers manning the office of Railway Board are mostly from organized Group a Railway Services and Railway Board Secretariat Service. IR is divided into 18 zones, headed by general managers who report to the Railway Board. The zones are further subdivided into 68 operating divisions, headed by divisional railway managers (DRM).
The divisional officers of the engineering, mechanical, electrical, signal and telecommunication, stores, accounts, personnel, operating, commercial, security and safety branches report to their respective DRMs and are tasked with the operation and maintenance of assets.
Policy and Procedures:
Centrally Administered Applications –
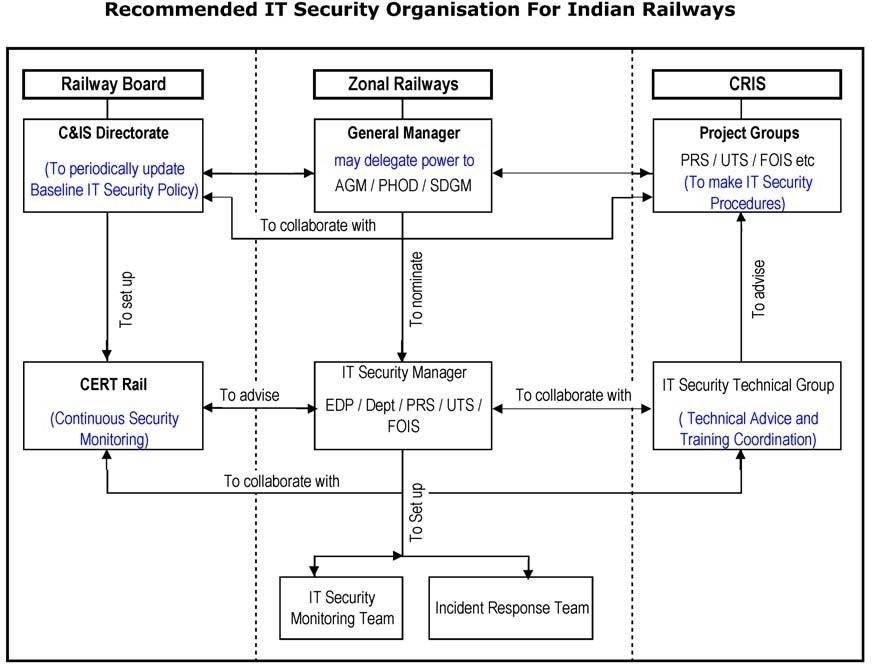
These are applications that are managed centrally by the organization’s IT department. Examples of such applications include Passenger Reservation System (PRS), Freight Operations Information System (FOIS), and Unreserved Ticketing System (UTS) in the Indian Railways. The IT security procedures for these applications are managed by the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS) or the Chief Information Security Officer (C&IS Dte) of Railway Board.
Example: PRS, FOIS, UTS
Zone-Based Applications –
These applications are managed by the Central Computer Agency (CCA) of the Railway Board or Zonal EDP Centers. Examples of such applications in the Indian Railways include Passenger Reservation and Information Management Environment (PRIME), Audit, Finance, and Revenue Expenditure System (AFRES), and Material Management Information System (MMIS). The IT security procedures for these applications are managed by the respective zone’s CCA or Zonal EDP Centers.
Example: PRIME, AFRES, MMIS
Distributed Applications –
These are applications that are spread across different locations and are managed by a centralized system. Examples of such applications in the Indian Railways include Management Information System (MIS) applications. The IT security procedures for these applications are managed by the MIS of Railway Board.
Example: MIS applications
Batch Type Applications –
These are applications that process data in batches at specific times. An example of such an application in the Indian Railways is the Payroll System, which processes employee salary data in batches. The IT security procedures for these applications are managed by the EDP centers.
Example: Payroll
General Purpose IT Equipment –
These are general-purpose IT assets such as personal computers (PCs) and servers that are placed in all offices. Concerned departments manage the IT security procedures for such assets.
Example: PCs, servers, placed in all offices

Auditee Environment
Structure of Mutual Fund
Typically, a mutual fund is a trust that pools the savings of a number of investors who share a common financial goal. The money collected is invested in capital market instruments such as, shares, debentures and other securities and money market instruments. The income earned through these investments and the capital appreciation realized is shared by its unit holders in proportion to the number of units owned by them. A mutual fund offers an opportunity to invest in a diversified, professionally managed basket of securities at a relatively low cost.
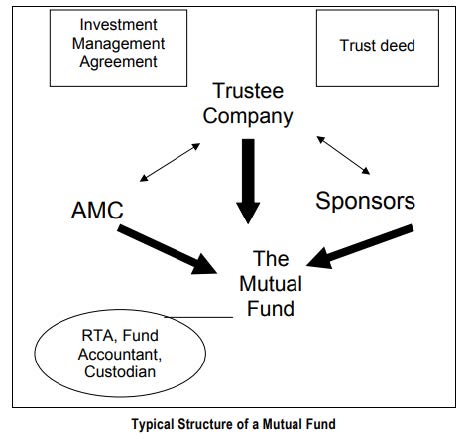
Sponsor
The Sponsor(s) are those who establish the Mutual Fund Trust and the Asset Management Company (AMC). They constitute the shareholders of the AMC.
Board of Trustees or Trustee Company
The trustees of a Mutual Fund could be constituted as a ‘Board of Trustees’ or could be incorporated as a ‘Trustee Company’ [‘Trustee Company’]. Where a Trustee Company is appointed, the duties of the trustee would be discharged through its directors. The Regulation 18 of MF Regulations has laid down the rights and obligations of the trustees. The Trustee Company is entitled to receive trusteeship fees for their services. The Sponsor appoints the trustees for the mutual fund. The trusteeship fee is paid by the mutual fund schemes and forms part of the overall expense ratio approved. The mutual fund’s assets belong to the investors and are held in fiduciary capacity for them by trustees. The Trustee Company is the epitome of corporate governance in mutual funds and the trustees are regarded essentially as the front-line regulator. The Trustee Company is entrusted with the responsibility of holding the property of the MF in trust for the benefit of the unit-holders.
Asset Management Company (AMC)
The AMC is a corporate entity, which floats, markets and manages a mutual fund scheme and in return receives a management fee paid from the fund corpus. The AMC is accountable to the Trust for its actions. Regulation 25 of MF Regulations has laid down the AMC’s obligations. In India, the Sponsor or the Trustee appoints the AMC through Investment Management Agreement (IMA). The contents of IMA are given in the Fourth Schedule to the MF Regulations. In terms of Regulation 24 of MF Regulations, no AMC can manage assets of more than one Mutual Fund and in case AMC decides to undertake any other activity then it has to satisfy SEBI that key personnel and infrastructure have been segregated activity-wise.
Fund Accountant (generally outsourced)
Fund Accountant is an entity handling the back office operations of the mutual fund for and on behalf of the AMC, viz., services related to fund accounting, purchase processing, corporate actions accounting, valuation and Net Asset Value (NAV) calculation, reporting and other incidental services in respect of the Mutual Fund. An AMC, generally, enters into service level agreement with Fund Accountant, if outsourced, which will clearly bring out the expectations from the third party service providers. Periodically, these would be reviewed to reflect at all times the business requirements currently in practice.
Audit Firm: DAR & Co. LLP
We are DAR & Co LLP (“Firm”), a professional firm since 2005 and providing services like Information System Audit (“IS Audit”), Statutory Audit, Internal Audit, Tax Audit, Consultancy for Project Finance and other related services.
In our Firm we have 3 Qualified Chartered Accountants and 2 semi qualified Chartered Accountants.
Partner’s Profile-
Mr. D
Qualification: CA, CWA, CS, DISA, and CISA.
Experience :
He has 12 years of experience in the fields of IS Audit, ERP Audit, and Central Bank Audit. As an expert in his field, he will be a valuable asset to any organization looking to manage their information security procedures.
Miss. A
Qualification: CA, DISA, CISA, and FAFD
Experience :
She brings with her a decade of experience in IS Audit, ERP Audit, and Forensic Audit. Her expertise and experience make her an ideal partner for any organization looking to manage their information security procedures and financial fraud detection.
Mr. R
Qualification: CA, DISA, CISA, CS, and FRM.
Experience :
He has 11 years of experience in the field of IS Audit and other regular statutory audits. His expertise and knowledge make him an ideal partner for any organization looking to manage their information security procedures and regulatory compliance requirements.
Auditee Environment
IT and Communication
RailTel Corporation of India Ltd. is a “Miniratna” (public sector) enterprise of Government of India focusing on providing broadband and VPN services. RailTel was formed with the objective of creating nationwide broadband, telecom and multimedia network, to modernize train control operation and safety system of Indian Railways.
CRIS manages most of the large centralized applications of Indian Railways. There are two aspects of the security system required in CRIS: firstly, the data of the important centralized applications such as Freight Operations Information System, Crew Management System, etc and the Passenger Reservation System, Unreserved Ticketing System, National Train Enquiry System etc residing in data centers managed by CRIS; secondly, the program code under development and maintenance for all these applications, which is maintained in the development centre in CRIS.
ITS Applications and Systems
- The IT applications and systems available today in Railways are:
- Ticketing and passenger service applications: the passenger reservation system PRS and the unreserved ticketing system UTS fall in this category. These applications cater to ticketing, reservation, and information needed by passengers to plan and execute the
- Freight and operations related applications: the freight operations information system FOIS, COIS, control office application, crew management system, etc falls in this
- MIS applications: such as asset management applications for all technical
- Finance and related applications: such as AFRES / PRIME, MMIS, personnel management system, operates statistics system, PAS, FAS, Small independent systems developed in various units of the Railways.
The IT assets of Indian Railways are being managed in the following basic ways:
- Centrally administered applications: such as PRS, FOIS, UTS have common hardware and software, with the core equipment placed either in one location (FOIS) or a few locations (PRS – 5, UTS– 7). This pattern is observed in up-coming applications such as COIS/ ICMS, Crew Management System, etc. The administration is done by C&IS Directorate of Railway Board and
- Batch-type applications: such as Payroll are being managed by the respective EDP centers, whether in Zonal headquarters, Divisional headquarters, PUs, or Workshops. These fall under the control of the CCA Directorate of Board.
- Zone based applications: such as PRIME, AFRES, MMIS are being managed by the respective Zonal EDP These also fall under the control of CCA Directorate of Board.
- Production Unit systems: All Production Units are based in one location only. All their systems are therefore managed by their local EDP / IT These applications are local to each Production Unit.
- Distributed systems: Systems such as the MIS applications, Control Office application, Workshop systems, are distributed: the servers are placed in the individual units, while the application logic is centrally developed and
- PCs, small servers, and other equipment: used for general information processing or running small home-made applications are being managed by the respective departments. These are not being directly managed by any Directorate of Board.
The information assets of the Indian Railways comprise all the individual elements of the above systems. These are:
- Hardware: Servers, PCs, printers, data storage devices, routers, switches, other network
- System software: Operating Systems, Database Management Systems, software application servers and web servers of different types, Office suites, email software, software development environments, compilers,
- Application software: Program codes (source code and object code) of applications written specially for Railways, whether in-house or outsourced. Program modules and components, program libraries, software classes and objects, customized interfaces and services, all form part of application software.
- Data / information: The data / information residing in the system, including transactions, logs, unstructured data, non-text data, emails, all are information assets. Data backed up or archived, along with the concerned logs and snapshots is also included.
- Documentation: System specifications, design documents, user manuals, policies of various kinds, records, printouts; both in paper form as well as on electronic media. Removable media containing system software and application software are also considered documentation for this purpose.
Background
In recent years, Indian Railways have implemented several large computerized Information Systems that are mission-critical in nature. In the meantime, incidents of unauthorized access to information, its unauthorized manipulation, unauthorized deletion, and denial of service to users, have increased tremendously all over the world.
As a result, IT Security has assumed great importance for Indian Railways. Traditionally, each individual IT application being used in Indian Railways has been designed to be fairly secure. However, organization-wide IT Security has not been put on a formal footing.
Situation
As railway industry has moved towards online reservation system due to the increased waiting time in big-big queue for reservation or cancellation of ticket so to away with the same railway has incorporated the same and to facilitate the smooth functioning of the same, some security controls was implemented to secure people data, money etc.,
We have identified following key issues in security controls. These are mentioned below:-
- Third party control was not checked for adding insurance company as vendor for providing insurance facility while booking ticket
- Security Controls was not tested properly while implementing the
- Timely review of control was not done so as to check whether the controls set are meeting the desired
- Irregularity in management of various
- Transaction beyond the specified time of
- Booking of accommodation on fictitious
- Deficits in applications controls.
Identified Problem Areas and Weakness
- The PRS had design deficiencies necessitating manual interventions during program terminations and link
- General controls comprising system documentation, sound IT security practices, change management and structured disaster recovery policy were There were deficiencies both in physical access and logical access controls. The total number of users with supervisory privileges was very high and booking clerks were also routinely assigned supervisory privileges, creating a risk of possible misuse of the powers associated with the privileges.
- Application controls were weak and a number of tickets were booked on fictitious details, indicating bogus/proxy booking in advance and thereby decreasing the availability of seats to genuine
- Validation checks for generation of pre-bought tickets, for journeys involving more than one lap, were weak. The system permitted generation of a zero value ticket for the second lap without generating the ticket for the first lap. Seats/ berths were also blocked for dummy passengers using the pre-bought
- The application software did not have validation checks to ensure compliance with the rules governing break
- Fares and distances were incorrectly adopted leading to incorrect levy of fares. The electronic databases contained numerous deficiencies rendering the data unreliable
- Even though allotment of berths was meant to be a zero error process, multiple instances were noticed where the system allotted the same berths to different
- Trains and stations were incorrectly defined in the system thereby preventing reservation of accommodation against them. The status of late running of trains was not set promptly leading to incorrect refunds to
Terms and Scope of Assignment
The IS audit would be with the objective of providing comfort on the adequacy and appropriateness of controls and mitigate any operational risks thus ensuring that the information systems implemented provide a safe and secure computing environment. Further, specific areas of improvement would be identified by benchmarking with the globally recognized best IT practices of COBIT framework. These terms of reference are based on the preliminary discussion the assignment team had with the On Track Limited team and is subject to further modification as required.
Broadly the scope of review primarily from security\controls and would involve checking whether:
- The acquisition and maintenance of hardware, communication network and software including system design were adequate and effective;
- The general controls were adequate and system was operating in an adequately controlled environment;
- The application controls were adequate and the system was in compliance with rules and adequately secured from possibilities of fraud;
- There was an effective mechanism to ensure most economic usage of available resources; and
- The accounting arrangements and control mechanism for credit card transactions were
For Railways, identity management is an important part of IT security. Therefore it has been separately treated by the core group. Identity management refers to identification, authentication, and authorization of persons who access any information system or data.
Identity Management systems consist of a combination of Public Key Infrastructure and other encryption methods, directory and discovery methods, and physical identification systems such as biometrics. Therefore the core group is of the view that a separate exercise should be undertaken by CRIS to set up Identity Management systems for the different applications and IT assets of Indian Railways.
Like in railways, for payment for ticket booking is authenticated by two-factor authentication. Also training in IT Security is required.
Logistic arrangements required
IS Auditor requires the following tools for audit:
A. Hardware:
A. Window based Systems, PDA and
B. Printers & other Printing
C. Scanners
D. Storage Media.
B. System Software:
System software will be selected according to client IT environment, so here auditor has to select the system software according to the IT environment in On Track limited. Auditor should use the original licensed version of system software, because it maintains the authenticity of data.
C. CAAT Tools :
a. Audit Software:
- IDEA Audit Software for data extraction
- Software Used at client site etc.
- Analyzer-Arbutus Software
- Pivot Tables for using Sampling
- Benford’s Law Test.
- Frequency Analysis.
- Audit Log.
D. Test data:
- Using Test Packs
- Using Integrated Test
Audit Scope and Methodology
The scope of audit included evaluation of the application and was primarily concerned with the transactions related to booking of tickets from the terminals operated by the railway personnel. Control Objectives for Information and related Technology (CoBIT) was referred to as a frame of reference for evaluation of the IT system. For application controls, ‘test data method’ including simulation and online enquiries were used to evaluate data validation and program logic. The reports generated by the PRS were
Also studied. Audit also selected data, as made available by the various zonal railways, for substantive checking of the completeness, integrity and consistency of data using Computer Assisted Audit Techniques namely, Interactive Data Extraction and Analysis (IDEA) and Structured Query Language (SQL).
Documents Reviewed
IT Security Audit policy
All major IT applications and assets, such as PRS, FOIS, UTS, Railnet, etc. should be audited by a certified third party IT Security auditing agency. The shortlist prepared by Cert-In of the Ministry of IT should be followed for this purpose.
- A list of the applications and assets to be considered for
- The IT Security Manager of the concerned unit will be responsible for ensuring that all the important IT applications / assets under his control are covered by a plan for IT Securit y
- IT Security audits can be carried out in a phased manner, with the most important applications being taken up
- Getting the IT Security audit conducted will be the responsibility of the designated agency / IT Security Manager for each such
- Identity Management Systems should be further explored by CRIS’ IT Security Technical Group, and the best options for enforcing appropriate Identity Management decided upon for the different categories of IT assets and
Major provisions of the IT Security standards ISO/IEC27002:2013 and ISO 27001:2005.
ISO/IEC 27002:2013 is the international standard for “Information technology — Security techniques — Code of practice for information security management”. It establishes guidelines and general principles for initiating, implementing, maintaining and improving information security management in an organization. It outlines control objectives and controls to enable an organization to meet the commonly accepted goals of information security management.
ISO/IEC 27001:2013 Information technology — Security techniques— Information security management systems Requirements provides a model for establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining and improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS) in an organization. It follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) model.
Management Review for ISO-27001 specifies that organizations should also get their ISMS reviewed annually by the Management Representative nominated for the purpose.
The ISMS should also be audited through authorized IT Security auditors at periodic intervals, normally two years.
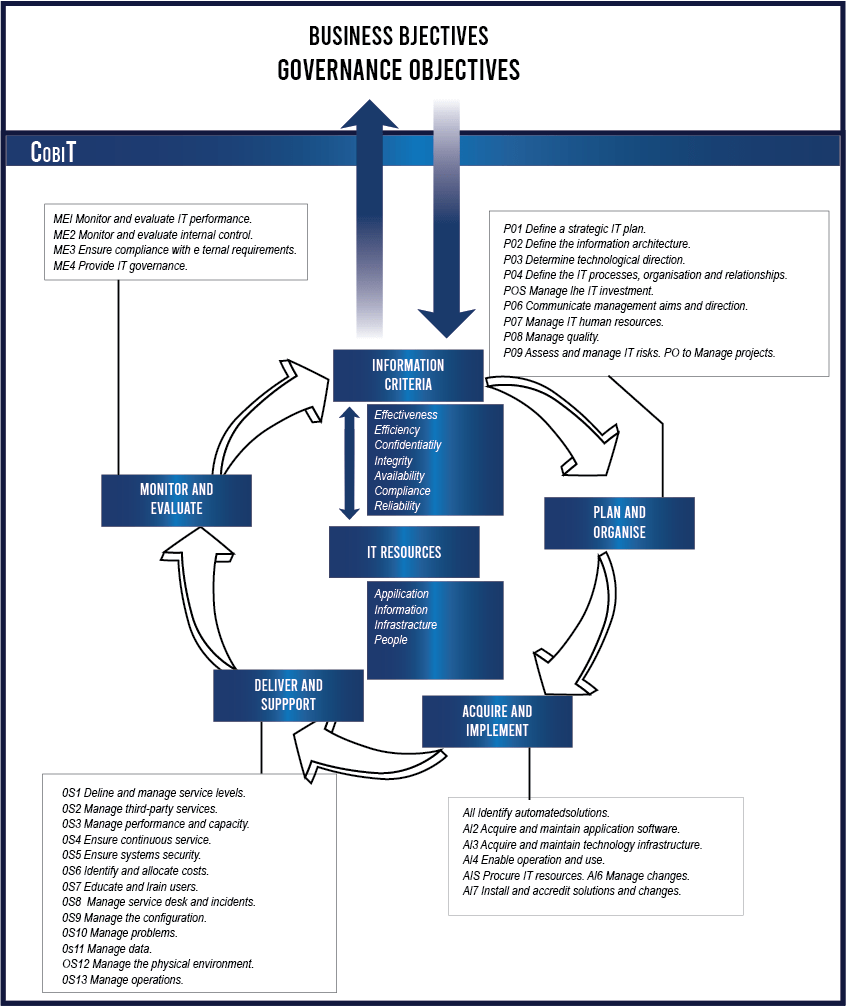
COBIT
IT Governance encompasses all the processes required to manage the IT assets of an organization to the optimum level, in order to obtain the best value from them. COBIT is a framework for IT Governance developed by the IT Governance Institute (ITGI) of the Institute of Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) based in USA.
Control Objectives for Information and related Technology (COBIT) provides good practices across a domain and process framework and presents activities in a manageable and logical structure. They are strongly focused more on control, less on execution. These practices will help optimize IT- enabled investments, ensure service delivery and provide a measure against which to judge when things do go wrong.
IT Security and IT Governance
References
For preparing this project, reference has been made to learning material of DISA course which includes the following:
- Technical guide on Information system audit issued by
- Information system Audit 0 – Module 1&2 issued by ICAI.
- isaca.org.
- icia.org
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indian_Railways
- Security policy for Indian Railways
Deliverables
- As discussed in the scope, we have covered following area in finding and recommendations;
- Ensuring all regulatory compliances as directed by Ministry of Railways and other regulatory requirements are complied
- Providing key issue identifying areas of control weakness in the security control implemented with recommendation for
- Providing final recommendation after discussion with the IT Department & management with confirmation of finding and agreed plan of
- Providing specific recommendation on security control, regular check, follow up and best practices, which can be adapted by railways as applicable.
- Providing guidelines that assist protection of confidentiality, availability and integrity of data of On Track
- Providing recommendation to, change the reservation method that needs the fingerprint of the one that goes for ticket booking so as to reduce railway reservation fraud and provide a lot of facilities to travelers and improve society. As a part of verification, TTE can verify the fingerprint of the passenger with stored data employing a standalone If the module can’t acknowledge the finger, this system will design to send an OTP to the concerned passenger’s registered mobile. A unique advantage of this paper automatically allocates the unoccupied passenger seat to the passenger who is the first on the waiting list by avoiding bribe for TTE to get a seat.
- Providing recommendation like Message will be sent to the passenger’s registered mobile with travel data before the journey. So, loss of identity cards or passwords isn’t a concern here. Also, nobody will travel through someone’s ticket. Passenger can get all details of the journey So that they don’t go to the station earlier to search the seat and coach no. It also saves the paper by not using the paper ticket. So it helps a lot to the environment.
Recommendations
- On Track limited should maintain the system documentation and manuals to enable referencing at the operational levels and develop a comprehensive IT policy encompassing IT Adequate physical access controls should be instituted to safeguard PRS assets and access controls should be strengthened to ensure accountability for transactions. Assignment of various privileges should be standardized and adequate controls need to be established to prevent misuse of privileges.
- On Track limited should institute a mechanism for incorporating changes promptly. A structured disaster recovery policy should be developed with off-site back up sites for business continuity as well as data storage. The PRS locations should be adequately protected from damage through fire, water
- On Track limited should build adequate checks to prevent reservation on fictitious or incomplete details and to enhance credibility and confidence in the system. Adequate validation checks should also be instituted for generation of pre-bought tickets. Any transaction of a pre-bought ticket for second lap should be validated with the details of the first lap of journey. The business logic and corresponding rules for break journey have to be adequately built into the system with validation checks to ensure
- On Track limited should strengthen its control mechanism to ensure that accommodation under various quotas is not misused and that unused accommodation in these quotas is taken back to the general pool systematically to optimize
- On Track limited should rectify the application, to correct the fare table and institute a mechanism at the appropriate level to ensure that distances between stations are uniformly adopted in the system, so that fares can be correctly levied. The inaccuracies in the master tables should also be rectified immediately to enhance reliability of data and to render generation of meaningful
- The software needs to be rectified to prevent multiple bookings against the same berth, as allotment of berths to passengers should be a zero error process. Suitable modifications in the program need to be carried out to provide compact accommodation for multi passenger reservation having a combination of confirmed reservation and waitlisted/RAC
- On Track limited should strengthen its control mechanisms to define the train profiles in the system as per the physical composition of trains. En route stations also have to be correctly defined for trains. Suitable mechanism should be developed to ensure that status of late running of trains is set promptly in the system so that cancellation charges are computed
- On Track Limited should improve its server
- Flexible booking timings can be implemented to reduce work load of
- Regular check on internal controls need to done, on monthly basis due to large coverage and to mitigate the risk and revenue leakage
Conclusion
The Passenger Reservation System is a prominent example of how Information Technology can be leveraged to provide transparency and convenience to users on a very large scale and is a pioneering e-governance initiative in the country. However, an IT enabled system on such a vast scale, also requires rigorous controls to sustain operations and to ensure that it is being run as intended, and complying with all the relevant rules and regulations. The system was found to have a few major design deficiencies and the areas of concern were related to system based and manual controls. These leave the system open to the risk of misuse adversely affecting the seat/berth availability to general passengers. The system also had design deficiencies which caused inconvenience to the passengers. Moreover, crucial areas covering security of the system and data, system and process documentation, database management, change management and user privilege management processes were either inadequate or poorly addressed.
DISA 3.0 Project Report on:
1. IS Audit of Banking Application
2. Migrating to cloud based ERP solution
3. Review of cyber security policies and procedure
4. Security and control risk assessment of toll bridge operations
5. System audit of a hospital automation system
6. Review of vendor proposal for SaaS services
7. Information Systems audit of a mutual fund systems
8. Audit of outsourced software development
9. Network security audit of remote operations including WFH
10. Infrastructure audit of a Bank data Centre
11. Conducting vulnerability assessment and penetration testing
12. Auditing Business continuity plan for Manufacturing system
13. Assessing risk and formulating policy for mobile computing
14. Auditing robotic process automation system
15. Implementation of adequate governance in hotel management system
16. Outsourced migration audit of merger of Banks
17. Audit of an E-Commerce web site
18. Audit of Online booking system for a hotel chain
19. Audit of Business Continuity Planning of a financial institution
20. Audit of online brokerage firm
21. Audit of Security Operation Centre of a Bank
22. Audit of Cyber Security Framework of a PSB
23. EVALUATION OF OUTSOURCING IT OPERATIONS
24. Auditing SWIFT operations in a Bank
25. Project Report Template and Guidelines on Project Report Submission
26. Information Systems Audit of ERP Software
27 .Implementing Grc As Per Clause 49 Listing Requirements
28. Review of IT Security Policies and Procedures in audit
