Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
A mutual fund is an open-end professionally managed investment fund that pools money from many investors to purchase securities. Mutual fund investors may be retail or institutional in nature. Mutual funds are often classified by their principal investments as money market funds, bond or fixed income funds, stock or equity funds, hybrid funds, or other. Funds may also be categorized as index funds, which are passively managed funds that match the performance of an index, or actively managed funds. In India, mutual funds are regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India, the regulator of the securities and commodity market owned by the Government of India. The mutual fund industry in India is growing at an exponential pace. The Indian mutual fund industry recorded an Average Assets Under Management (AAUM) of Rs. 23.16 trillion as on February 28, 2019. The AUM of the industry stood Rs. 5.09 trillion on February 28, 2009, which means the Indian mutual fund industry has registered a more than 4 ½ fold increase in a period of 10 years.
There are as many as 44 AMFI (Association of Mutual Funds in India) registered fund houses in India which together offer more than 2,500 mutual fund schemes. The wide array of funds often make it a little difficult for investors to choose the best scheme for them. To ease this process, we list out the 10 most popular mutual fund houses in India.
The mutual fund industry in India is dominated by
HDFC Mutual Fund
HDFC Mutual Fund is the largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 3,42,525 crores. The company has been consistently performing well in the market and has managed to maintain its position as the leader in the industry. With a wide range of funds catering to different investment objectives and risk profiles, HDFC Mutual Fund has become a popular choice among investors.
ICICI Prudential Mutual Fund
ICICI Prudential Mutual Fund is the second largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 3,21,281 crores. The company has a diverse portfolio of funds that cater to different investment needs of investors. With a focus on transparency, customer service, and strong investment performance, ICICI Prudential Mutual Fund has established itself as a reliable and trusted name in the industry.
SBI Mutual Fund
SBI Mutual Fund is the third largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 2,84,124 crores. The company has a strong presence in both equity and debt markets and has a wide range of funds catering to different risk profiles and investment objectives. With a focus on innovation and customer service, SBI Mutual Fund has been able to attract a large number of investors over the years.
Aditya Birla Sun Life Mutual Fund
Aditya Birla Sun Life Mutual Fund is the fourth largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 2,46,696 crores. The company has a diverse portfolio of funds that cater to different investment objectives and risk profiles. With a focus on innovation and superior customer service, Aditya Birla Sun Life Mutual Fund has been able to build a strong brand presence in the industry.
Reliance Mutual Fund
Reliance Mutual Fund is the fifth largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 2,34,293 crores. The company has a wide range of funds catering to different investment needs and has a strong presence in both equity and debt markets. With a focus on performance and customer satisfaction, Reliance Mutual Fund has been able to build a loyal customer base over the years.
UTI Mutual Fund
UTI Mutual Fund is the sixth largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 1,59,694 crores. The company has a long and established history in the industry and has been able to maintain its position in the market over the years. With a diverse portfolio of funds and a strong focus on customer service, UTI Mutual Fund has been able to build a loyal customer base.
Kotak Mahindra Mutual Fund
Kotak Mahindra Mutual Fund is the seventh largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 1,50,271 crores. The company has a wide range of funds catering to different investment needs and has a strong presence in both equity and debt markets. With a focus on customer service and innovative products, Kotak Mahindra Mutual Fund has been able to attract a large number of investors over the years.
Franklin Templeton Mutual Fund
Franklin Templeton Mutual Fund is the eighth largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 1,19,933 crores. The company has a long and established history in the industry and has been able to build a loyal customer base. With a focus on strong investment performance and customer service, Franklin Templeton Mutual Fund has been able to maintain its position in the market.
Axis Mutual Fund
Axis Mutual Fund is the ninth largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 89,768 crores. The company has a diverse portfolio of funds catering to different investment objectives and risk profiles. With a focus on innovation and customer service, Axis Mutual Fund has been able to attract a large number of investors over the years.
DSP Mutual Fund
DSP Mutual Fund is the tenth largest mutual fund house in India with assets under management (AUM) of Rs. 78,363 crores. The company has a wide range of funds catering to different investment objectives and risk profiles. With a focus on strong investment performance and customer service, DSP Mutual Fund has been able to build a loyal customer base over the years. The company also emphasizes research-driven investment management and has a team of experienced fund managers who analyze market trends and make informed investment decisions. Additionally, DSP Mutual Fund offers innovative investment solutions and online platforms to make investing easier and more accessible to its customers.
How Do Mutual Fund Works
While you might have heard many experts say that investing in mutual funds is one of the best ways to grow your wealth, it is perhaps even more important to know how mutual funds work. Let’s understand the working of mutual funds right from the time an Asset Management Company (AMC) or fund house decides to launch a mutual fund till it starts giving attractive returns:
- 1. The process begins when a fund house identifies a potential money- making opportunity in the market subject to key risks.
- 2. The fund house then weighs the newly identified opportunity against existing investment opportunities and analyses how it can add further value for current investors.
- 3. The fund house then appoints a fund manager who creates a portfolio of different asset classes including equities, debt and money market securities. The asset allocation of the scheme decides under which mutual fund category the scheme will fall – Equity Fund, Debt Fund or Hybrid Fund.
- 4. The fund manager then compiles all the details including the scheme’s asset allocation, risk level, etc in a document and files the draft with market regulator SEBI for its approval.
- 5. After receiving SEBI’s approval, the fund house makes the scheme available to the public for subscriptions through a New Fund Offer (NFO). An NFO generally lasts for 7-10 days.
On the basis of the subscription period, mutual fund schemes can be classified as open-ended and close-ended schemes. An open ended mutual fund scheme allows investors to enter and exit the fund anytime even after the closure of the NFO period. Whereas, a close-ended fund allows investors to enter into the scheme only during the NFO period and does not allow them to exit it until maturity which is typically 3-4 years from the launch date.
- 1. After receiving the initial subscription, the fund manager manages the scheme actively or passively depending on the scheme’s requirements as well as market/economic conditions.
- 2. A mutual fund investment provides earning to its investors in the form of dividend payouts and capital gains.
About Mutual Fund Service System (MFSS)
An investor who wishes to subscribe or redeem units of a mutual fund scheme can now use Mutual Fund Service System (MFSS) provided by NSE.
This service has been launched on November 30, 2009 at the hands of Mr C B Bhave, Chairman, Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI), on November 30, 2009.
Mutual Fund Service System
Mutual Fund Service System (MFSS) is an online order collection system provided by NSE to its eligible members for placing subscription or redemption orders on the MFSS based on orders received from the investors.
Orders Placing
The MFSS will be available for Participants between 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
The NSE MFSS shall facilitate entry of both buy and sell orders. In order to subscribe units, member will be required to place buy orders. A member who wishes to redeem units of mutual fund scheme will be required to place sell orders in the system. Participants can choose between Physical mode and depository mode while putting their subscription / redemption requests on the MFSS. All orders shall be settled on order to order basis, on T+1 (working days).
Individuals, HUF and Body Corporate can participate in MFSS subject to completing the KYC procedure. In case of a minor the guardian would have to be KYC compliant.
Confirmation of order
The system will generate an order confirmation slip for each order which includes time stamp of the order being put on the system, on behalf of the investor. The order confirmation slip which is generated by the system shall be given to the investor by the member and is the conclusive evidence of the transaction.
To deal with the challenges arise in Mutual Fund Service System (MFSS) of (KAA Asset Management Limited), they have appointed M/s AKA & Associates, a Firm of Chartered Accountants, to review and audit of Information System in place and provide suitable recommendations for improvements & best practices that can be adopted in the System of Mutual Funds.
Audit Engagement Team
Our approach to selecting the right people for a project is to bring together the necessary skills and experience for a particular assignment from the rich mix of skills and experience available. The assignment will be executed by M/s AKA & Associates under the personal supervision and lead by Mr K. M/s AKA & Associates is one of the leading practitioners in the area of IS audit, comprising of the following main team members:
1. Mr K –Team leader (DISA qualified, having an experience of over 10years in IS audit). He has worked on 10+ SAP Engagements across different industries like FMCG, Telecom, Chemicals, Oil & Gas, Professional Services, Insurance etc., performing key leadership roles of Program/Project Management.
2. Ms A, Mr A, Ms D, Mr M –Team members (All of the team members are DISA qualified and are experts in the field of audit of software development projects for a period of 5-8 years and have worked on various Projects providing SAP solutions for various aspects and other statutory compliances.
The said team has handled various other projects concerning IS audits and have been into consultation of Software Development Life Cycle, Migration Audits, Business Continuity Management etc.
Auditee Environment
Structure of Mutual Fund
Typically, a mutual fund is a trust that pools the savings of a number of investors who share a common financial goal. The money collected is invested in capital market instruments such as, shares, debentures and other securities and money market instruments. The income earned through these investments and the capital appreciation realized is shared by its unit holders in proportion to the number of units owned by them. A mutual fund offers an opportunity to invest in a diversified, professionally managed basket of securities at a relatively low cost.
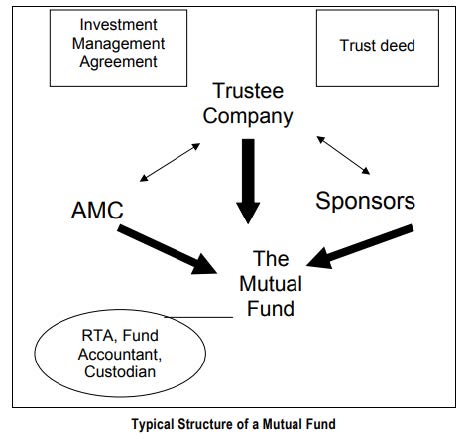
Sponsor
The Sponsor(s) are those who establish the Mutual Fund Trust and the Asset Management Company (AMC). They constitute the shareholders of the AMC.
Board of Trustees or Trustee Company
The trustees of a Mutual Fund could be constituted as a ‘Board of Trustees’ or could be incorporated as a ‘Trustee Company’ [‘Trustee Company’]. Where a Trustee Company is appointed, the duties of the trustee would be discharged through its directors. The Regulation 18 of MF Regulations has laid down the rights and obligations of the trustees. The Trustee Company is entitled to receive trusteeship fees for their services. The Sponsor appoints the trustees for the mutual fund. The trusteeship fee is paid by the mutual fund schemes and forms part of the overall expense ratio approved. The mutual fund’s assets belong to the investors and are held in fiduciary capacity for them by trustees. The Trustee Company is the epitome of corporate governance in mutual funds and the trustees are regarded essentially as the front-line regulator. The Trustee Company is entrusted with the responsibility of holding the property of the MF in trust for the benefit of the unit-holders.
Asset Management Company (AMC)
The AMC is a corporate entity, which floats, markets and manages a mutual fund scheme and in return receives a management fee paid from the fund corpus. The AMC is accountable to the Trust for its actions. Regulation 25 of MF Regulations has laid down the AMC’s obligations. In India, the Sponsor or the Trustee appoints the AMC through Investment Management Agreement (IMA). The contents of IMA are given in the Fourth Schedule to the MF Regulations. In terms of Regulation 24 of MF Regulations, no AMC can manage assets of more than one Mutual Fund and in case AMC decides to undertake any other activity then it has to satisfy SEBI that key personnel and infrastructure have been segregated activity-wise.
Fund Accountant (generally outsourced)
Fund Accountant is an entity handling the back office operations of the mutual fund for and on behalf of the AMC, viz., services related to fund accounting, purchase processing, corporate actions accounting, valuation and Net Asset Value (NAV) calculation, reporting and other incidental services in respect of the Mutual Fund. An AMC, generally, enters into service level agreement with Fund Accountant, if outsourced, which will clearly bring out the expectations from the third party service providers. Periodically, these would be reviewed to reflect at all times the business requirements currently in practice.
Background
The audit should be encompassing audit of systems and processes, inter- alia, related to examination of integration of front office system with the back office system, fund accounting system for calculation of net asset values, financial accounting and reporting system for the AMC, Unit-holder administration and servicing systems for customer service, funds flow process, system processes for meeting regulatory requirements, prudential investment limits and access rights to systems interface.
Mutual Funds / AMCs are advised to conduct their systems audit on an annual basis by an independent CISA / CISM qualified or equivalent auditor to check compliance of the provisions of the circular
Mutual Funds / AMCs are further advised to take necessary steps for the exception report. The exception report should be placed for review to the Technology Committee before it placed to the AMC & Trustee Board. Thereafter, exception observation report along with trustee’s comments starting from the financial year April 2019 – March 2020 should be communicated to SEBI within six months of the respective financial year. Further, System Audit Reports shall be made available for inspection.
The circular is issued in exercise of powers conferred under Section 11 (1) of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992, read with the provisions of Regulation 77 of SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations, 1996, to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote the development of, and to regulate the securities market
Situation
As the Mutual fund market have moved towards online Investment & Trading system for ease of its investors by eliminating offline representative intervention for investing, buying or selling of mutual funds and easy access for trading to its investors anywhere and everywhere it implemented various security controls to secure its user data by maintaining Integrity, confidentiality and availability by implementing specific controls as and where required.
KAA Mutual Fund is manned by around 2000 people. There are 220 applications running and around 150 plus network devices like firewall, IDS, IPS, Router, Switches, Gateways etc. are there along with 500 plus high end servers. Appropriate communication lines with all required redundancies are present.
Information security risk management policy maintained by the enterprise is not updated and not reviewed for the last three years. At the time of hiring the employees, no background check is done and no documents are asked to submit. Hiring policies are not defined in line with IT Operation.
Management says there are no issues with Access control mechanism. But, multiple failure attempts by unauthorized users were found, it was informed to the senior management but Management did not take any actions believing that these are just unsuccessful attempts therefore no follow-up action is required.
Testing of Security patches for application servers were not being performed before deploying into production environment. There are also issues with the management of backup tapes and blank tapes.
Occasionally, huge rush is observed during the peak closing time of the market especially on Friday. And server is seen experiencing down-time.
Any unusual activities observed by the IT Personnel are reported to CISO by following the proper formal procedure designed by the top management.
No training is provided to employees like Mock drill of earthquake/ fire, safety program classes to its staff. Since, management believes that these circumstances never appeared in the lifetime of the company.
Scope and Terms of assignment
We have been appointed by KAA MF by letter dated 06th April 2021 for the Information System Audit of Mutual fund System on the scope and terms mentioned in the engagement are here under.
Scope:
1. Review adequacy of internal control systems and confirm its appropriateness
2. Review functioning of internal audit function, reporting structure coverage and frequency of internal audit and identify areas requiring improvement.
3. Review financial and risk management policies as per corporate governance requirements and its adequacy.
4. Review compliance requirements as per Information Technology Act as amended in 2008.
5. Review whether the current risk management strategy is adequate considering the current and future business plans, business process, technology deployed, organization structure and regulatory requirements.
Other terms and conditions
1. The report should be submitted latest within three weeks from the date of offer letter.
2. The consolidation remuneration shall be Rs. 1,00,000 (Rupees One Lakh only). It is a package payment and no other travelling or any other allowance will be paid.
3. The auditor is not disqualified in under provision of Companies Act,2013.
4. The auditor firm have never been depaneled due to poor performance.
5. The audit is to be conducted by a CISA, DISA qualified Chartered Accountant or by a team to be headed by the CISA, DISA qualified Chartered Accountants.
6. In case any major ambiguities is noticed or detected, it must be reported to board by the fastest available mode of communication or personally, if Stationed, locally.
Logistics arrangements required
KAA MF shall appoint one senior IT officer part of the implementation team and operation head to co-ordinate for finalizing the initial work plan and shall continue to work with the audit team as when required till the completion of assignment. The company shall make available necessary systems, software, software resources and support facilities for completing the assignment within the appointed time. During the course of audit the following resources shall be made available:
1 2 Nodes with Read only access to extract reports from application.
2 One Laptop with Windows 10 / Microsoft office 2013.
3 Adequate seating and storage for the team.
4 Facilities and permissions to have discussion and seek informations from the IT department as well as the different user departments members.
5 Permission to do penetration testing on the system
6 Permission to carry our Laptop with Computer Aided Audit tools installed to be used for our data analysis.
Methodology and Strategy adopted for the audit
Our audit team has executed the assignment and performed audit procedures on the basis of the following audit methodologies and strategies:-
1. In depth study and analysis of all aspects of application software to obtain understanding how the system currently operates.
2. Reviewed the software in operation to understand how the various components of system interact with each other.
3. Tested each modules in the system including the documentation prepared in respect of each.
4. Reviewed the inbuilt controls for stored data so as to ensure that only authorized persons have access to data on computer files.
5. Reviewed the process and policy of taking backup of data i.e. disk mirroring and its restoration process.
6. Review the alternate activities performed during system downtime and its mapping and data merger process for further continuance of regular operations.
7. Reviewed the controls established which ensure that all the transactions are entered and accepted for further processing and that any transactions are not processed twice.
8. Reviewed the controls established so as to ensure that only valid transactions are processed.
Documents Reviewed
While performing audit procedures, we reviewed the following documents:
➢ Organization structure Diagram.
➢ List of Hardware, Software and Application Software currently used by the client.
➢ Service Offer Agreement.
➢ Password Policy.
➢ Business Continuity Plan and Disaster Recovery Plan.
➢ Information Security Policy.
➢ Backup Procedures.
➢ User Creation, modification and deletion Policy.
➢ Various MIS reports and exception reports generated by the system.
➢ Information system asset registers
References
➢ ISO 27001
➢ COBIT 2019 Framework
➢ Guidelines and Circular issued by SEBI
➢ Information Technology Assurance Framework issued by ISACA
➢ GTAG (Global Technology Audit Guide) prepared by the Institute of Internal Auditors.
➢ Information Technology (Amendment) Act,2008.
➢ References to the ISA Study Materials issued and provided by ICAI
Deliverables
Our audit team has provided following deliverables to the company after
completion of assignment :-
a) Final IS Audit Report drafted in pursuance to ISACA and COBIT Framework stating that such audit has been conducted as per the guidelines issued by SEBI in order to express an opinion on effectiveness of operations and controls of Mutual Fund Systems
b) Executive Summary for senior management persons.
c) Detailed finding and recommendations related to the IS Audit for continuity of sound and stable information system, protection of mutual fund unit holders, market efficiency, privatization and opening of markets, etc.
d) Meeting of IS Security needs
e) Assess risks, economy, efficiency and quality
Audit Findings and Recommendations
Information Security Risk Management Control
The audit procedure conducted for this control objective was observation and confirmation. It was observed that the information security risk management process was last reviewed by the top management three years ago. Several management action plans might have become irrelevant and outdated, which may now require changes. This could pose a high risk to confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets. The recommendation for this control objective is to define a process for information security risk management that should be followed annually.
Human Resource Control
The audit procedure for this control objective was inquiry and inspection. It was observed that background check procedures were not performed for all new joiners subject to hiring documents of employees who are given authorized access to the Stock Brokers/ Depository Participant’s critical systems, networks, and other computer resources. This may result in serious consequences, such as fraud. The nonavailability of employees’ background may lead to stringent supervision, monitoring, and access restrictions. This could pose a high risk to confidentiality and availability of information assets. The recommendation for this control objective is to define hiring policies in line with IT operations and perform background check procedures for all new joiners.
Access Control
The audit procedure for this control objective was inspection, observation, and confirmation. It was observed that many unauthorized user access attempts were found from system logs which were attempted and failed multiple times. Unauthorized user access may even get access to confidential data after trying multiple times. This could pose a high risk to confidentiality and integrity of information assets. The recommendation for this control objective is to implement access account lock policies after three failure attempts for all accounts.
Patch Management Control
The audit procedure for this control objective was observation and confirmation. It was observed that testing of security patches is not carried out by IT personnel at regular intervals. This may create a risk to production environment and other systems adversely. This could pose a medium risk to confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets. The recommendation for this control objective is to perform rigorous testing of security patches before deployment into the production environment to ensure that the application of patches does not impact other systems.
Backup Media Management Control
The audit procedure for this control objective was observations and confirmation. It was observed that backup tapes are not leveled accurately externally and internally and stored in humid conditions within the data center. Incorrect leveling will lead to incorrect processing leading to data integrity issues. This could pose a medium risk to confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets. The recommendation for this control objective is to check all tapes for internal and external levels and store them in a secure condition in the offsite premises.
Business Continuity Controls
The audit procedure for this control objective was business continuity policy documents MIS reports. During peak closing time of the market, if the server experiences downtime due to a large number of user login at the same point of time, it could pose a medium risk to integrity and availability of information assets. In case of a prolonged or frequent service disruption, customers may lose confidence resulting in loss of faith and goodwill. The recommendation for this control objective is to install extra servers and workstations to manage workload during peak hours. Appropriate physical and logical access controls also need to be implemented on the same.
Governance Control
The audit procedure for this control objective was observation and inquiry. It was observed that sometimes unusual activities detected by IT personnel may be too serious that immediate actions might be required. There is a time lag between identification and reporting of unusual activities and events to the CISO or to the senior management. Due to extreme reporting procedures performed, it may lead to delay, but reporting of unusual activities and events to the CISO is higher than usual. This could pose a high risk to availability of information assets.
Disaster Recovery Plan
The audit procedure for Disaster Recovery Plan included inspection and observation. The risk ranking for this control objective is medium. During the audit, it was observed that the company has never provided any sort of disaster-related training, such as mock drills for earthquakes or fires, or safety program classes to its staff. Though the chances of a disaster are very low in this region, if it were to happen, it would be very difficult to manage the situation. Therefore, proper training must be given to employees as to how to respond to disasters, and mock drills must be performed at least once a year.
Conclusion
Based on the IS Audit review and findings, the overall conclusions on specific areas are as Follows:-
Information security Risk Management Control
We have observed that the information security control in KAA Mutual Fund working effectively. Further The areas where controls need to be strengthened are highlighted in Para 11 of our Report.
Access Controls, Application & Database Controls
Our review of Access controls at the IT Environment as implemented in KAA Mutual Fund Company using Windows Server, Oracle and MFSS confirms that appropriate security and access controls have been implemented by using related functions and features of the software. Our test checks have revealed that systems of security and controls are reliable.
However, there are some cases of old investors accounts not Deactivated which does not have any balances in their funds.
In addition, we found scope of improvement in the MFSS Software so that manual event update can be avoided at Mutual Funds to prevent revenue leakage.
Also, there is missing data relating to periods when system was not available which have not been updated in the revenue tables in database which may impact correct revenue recognition & risk of revenue loss.
Environmental Controls and Business Continuity plan
Our review of Environmental Controls and BCP implemented by KAA Mutual Fund Company confirms that the business continuity plan is implemented and the staff is aware of various disaster situations.
The power backup for IT Server and Air-conditioner can be improved.
One critical gap is absence of an alternate disaster recovery site and related documentation, which should provide for back up and off-site location of application software, data files and system software to facilitate their restoration following the recovery of critical application.
Further Action
We consider that the recommendations given in our IS Audit Report read together with audit findings to this report would be very useful for facilitating business process controls of KAA Mutual Fund Company and will aid in improving the effectiveness of the MFSS operations. We would like to affirm that the matters included in this report are those which came to our notice during our review by following normal Information System audit procedures by complying with Globally Applicable Information Systems Auditing Standards, Guidelines and procedures that apply specifically to Information system auditing issued by information systems audit and control association, USA and Security and Control practices as outlined in COBIT- 2019 issued by ISACA as adopted to KAA Company operations. Further on account of limitations of scope and time, we have used sample test and test check approach. Hence, certain areas, which are outside the scope of review such as source code review, implementation control are not covered.
DISA 3.0 Project Report on:
1. IS Audit of Banking Application
2. Migrating to cloud based ERP solution
3. Security control review of railway reservation system
4. Review of Cyber Security Policies and Procedures Disa ICAI Project Report ISA 3.0
5. Disa Project Report on Security and Control Risk assessment of Toll Bridge operations
6. System audit of a hospital automation system
7. Review of vendor proposal for SaaS services
8. Audit of outsourced software development
9. Network security audit of remote operations including WFH
10. Infrastructure audit of a Bank data Centre
11. Conducting vulnerability assessment and penetration testing
12. Auditing Business continuity plan for Manufacturing system
13. Assessing risk and formulating policy for mobile computing
14. Auditing robotic process automation system
15. Implementation of adequate governance in hotel management system
16. Outsourced migration audit of merger of Banks
17. Audit of an E-Commerce web site
18. Audit of Online booking system for a hotel chain
19. Audit of Business Continuity Planning of a financial institution
20. Audit of online brokerage firm
21. Audit of Security Operation Centre of a Bank
22. Audit of Cyber Security Framework of a PSB
23. EVALUATION OF OUTSOURCING IT OPERATIONS
24. Auditing SWIFT operations in a Bank
25. Project Report Template and Guidelines on Project Report Submission
26. Information Systems Audit of ERP Software
27 .Implementing Grc As Per Clause 49 Listing Requirements
28. Review of IT Security Policies and Procedures in audit
