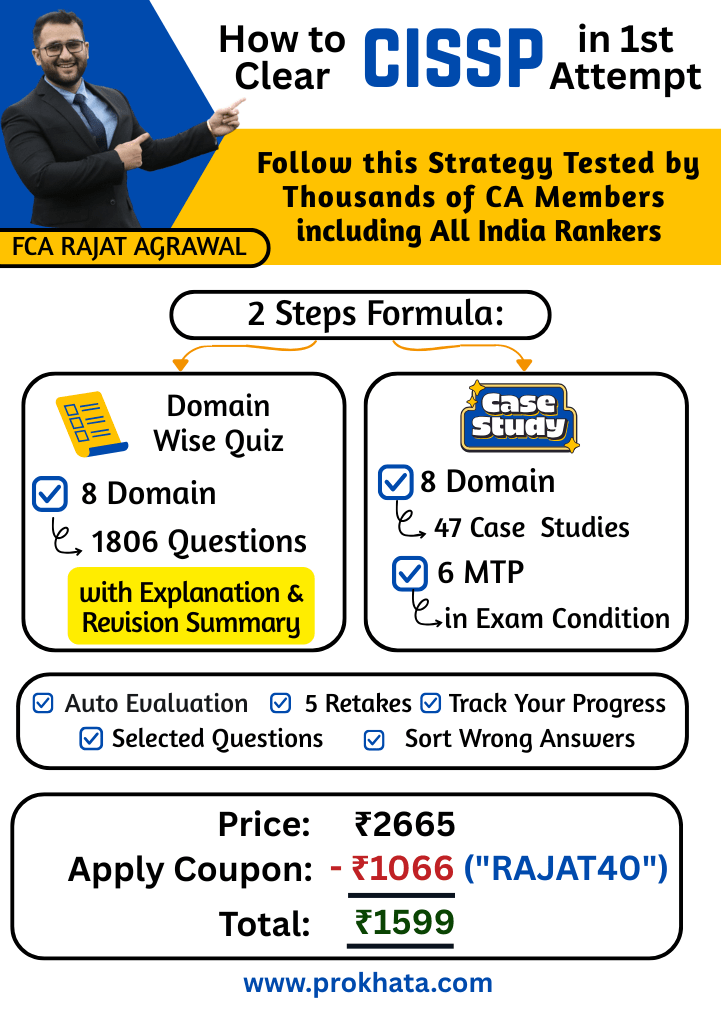
Course Outline
Our Domain-wise quizzes cover all the important topics that are most frequently asked in exams
Module 1: Foundations of Information Security
- Introduction to Key Concepts:
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA Triad)
Nonrepudiation
Security Principles: Least Privilege, Need to Know, Separation of Duties, Defense in Depth
Due Care and Due Diligence
- Risk Management:
Risk Definitions: Inherent Risk, Residual Risk, Threat, Vulnerability, and Risk
Risk Management Strategies: Avoidance, Mitigation, Acceptance, Transference
Risk Assessment: Qualitative and Quantitative
Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE)
Risk Calculation and Analysis
Risk Management Frameworks: NIST
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery:
Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Business Continuity Planning (BCP)
Cold, Warm, and Hot Sites
Business Continuity vs. Disaster Recovery
Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
Disaster Recovery Testing
Module 2: Security Controls and Mechanisms
- Types of Security Controls:
Physical Controls
Preventive Controls
Detective Controls
Compensating Controls
- Access Control:
Authentication, Authorization, Identification, and Accountability
Access Control Models: DAC, MAC, RBAC, ABAC, Rule-BAC
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Biometrics
Kerberos
RADIUS and TACACS+
Session Management
- Physical Security:
Physical access controls (e.g. locks, proximity cards, mantraps)
Intrusion detection systems
CCTV systems
Environmental controls
Module 3: Data Security and Protection
- Data Classification:
Classification Levels (Commercial and Government)
Data Labeling
- Data Handling:
Data in Transit, Data at Rest, and Data in Use
Data Aggregation
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Cryptography:
Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption
Hashing Algorithms
Digital Signatures and Certificates
Key Management
- Data Lifecycle Management:
Data Collection, Maintenance, Retention, and Disposal
Data Remanence
Data Removal Techniques
Module 4: Network Security
- OSI Model:
Layer Functions (Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application)
Encapsulation
- Network Protocols:
TCP/IP
IPsec, TLS, VPNs
Wireless Security (WPA2, WPA3, etc.)
Authentication Protocols (RADIUS, CHAP, PAP)
- Network Devices and Architectures:
Firewalls, Routers, Switches
VLANs
Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Zero-Trust Network
- Network Monitoring:
NetFlow
Module 5: Software and Application Security
- Software Development Methodologies:
Waterfall, Agile, Spiral, RAD
DevOps
Software Testing (Unit, Integration, Acceptance)
Security Testing (DAST, SAST, Fuzzing)
- Cloud Computing:
SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, FaaS
Shared Responsibility Model
- Common Vulnerabilities and Attacks:
SQL Injection
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Buffer Overflow
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
Ransomware
- Security Controls and Techniques:
Input Validation
Parameterization
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
TLS encryption
Module 6: Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Key Laws and Regulations:
GLBA, PCI DSS, HIPAA
Module 6: Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Key Laws and Regulations:
GLBA, PCI DSS, HIPAA, FISMA, GDPR
DMCA, COPPA, CALEA, Economic Espionage Act
State Data Breach Laws
- Intellectual Property:
Copyright, Trademark, Patent, Trade Secret
- Data Privacy:
Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Protected Health Information (PHI)
- Incident Response and Forensics:
Incident Response Phases
Evidence Handling
Computer Forensics
Legal Admissibility of Evidence
Module 7: Security Program Management & Other Important Concepts
- Security Program Management:
ISO 27000 Series, COBIT
Security Awareness Programs
Security Baselines
Change Management
- Data Roles and Responsibilities:
Data Owner, Business Owner, System Owner, Data Processor, Data Custodian, Administrator, Data Subject
- Supply Chain Risk
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Module 8: Security Testing, Operations and Monitoring
- Security Testing and Vulnerability Assessment
Types of testing: Black-box, Gray-box, White-box
Vulnerability Scanning and Penetration Testing
- Risk Management and Compliance
Business Impact Analysis
Auditing and Risk Assessment
- Security Operations and Monitoring
Log Management and Monitoring Techniques
SIEM, IAM
- Software Development and Testing
Code Coverage, Code Review
- User Account Management
Assessments
Quizzes after each module summary
Mock test papers
A comprehensive final exam
This structure allows for a logical progression from foundational concepts to more specialised topics.
CISSP Certification Course
What is CISSP certification?
The International Information System Security Certification Consortium (ISC)2, which offers the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification, is a well-known name in information security. It is a vendor-neutral certification that verifies a person’s information security and assurance knowledge and skills.
The eight information security domains covered by the CISSP certification include security and risk management, asset security, communication and network security, identity and access management, security assessment and testing, security operations, and software development security. These topics are all covered by the CISSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK), which is a list of the topics covered by the certification.
The ability to create, execute, and manage a complete information security programme is demonstrated to peers, clients, and employers by having a CISSP certification. In the subject of information security, it is highly respected and frequently a prerequisite for senior-level information security roles.
The CISSP certification is good for three years, and it must be kept up to date by earning Continuing Professional Education (CPE) credits.
What is the purpose of CISSP?
The CISSP covers all of the essential components of the cybersecurity industry, including security and risk management, network and communication security, security testing, and security operations.
What is the eligibility for CISSP certification?
To be eligible for the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification, you must meet the following criteria:
1.Work Experience: Have at least 5 years of cumulative, paid work experience in two or more of the 8 CISSP domains as outlined by the CISSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK).
2.Education: Hold a minimum of a high school diploma, or equivalent, although having a higher level of education, such as a bachelor’s or master’s degree, may substitute for one year of work experience.
3.Endorsement: Obtain endorsement from an existing CISSP who can vouch for your professional experience and knowledge.
4.Agree to the (ISC)² Code of Ethics: Agree to adhere to the (ISC)² Code of Ethics, which requires certified individuals to act with integrity, use their knowledge for the betterment of society, and maintain the highest standards of professional conduct.
By meeting these eligibility requirements, you can demonstrate to (ISC)² and the information security community that you have the necessary knowledge, experience, and commitment to become a Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
Course Prerequisites and Goals
Prerequisites:
To earn this certification, you must pass the exam as well as have 5 years of paid experience in two or more domains of the CISSP Common Body of Knowledge. However, if you have passed the examination but are short of the requisite experience, you can become an Associate of (ISC) 2 . Thereafter, you will have 6 years’ to earn the requisite experience. Study Resources: All supplemental materials will be provided in the ‘resources’ tab of the course page!
Course Goals
By the end of this course, students should be able to:
❏ Pass the CISSP Exam